The p2d2 Cycle
The p2d2 cycle describes the bidirectional data flow between administration, OpenData portal, p2d2 community, and public data platforms. The process consists of 9 steps:
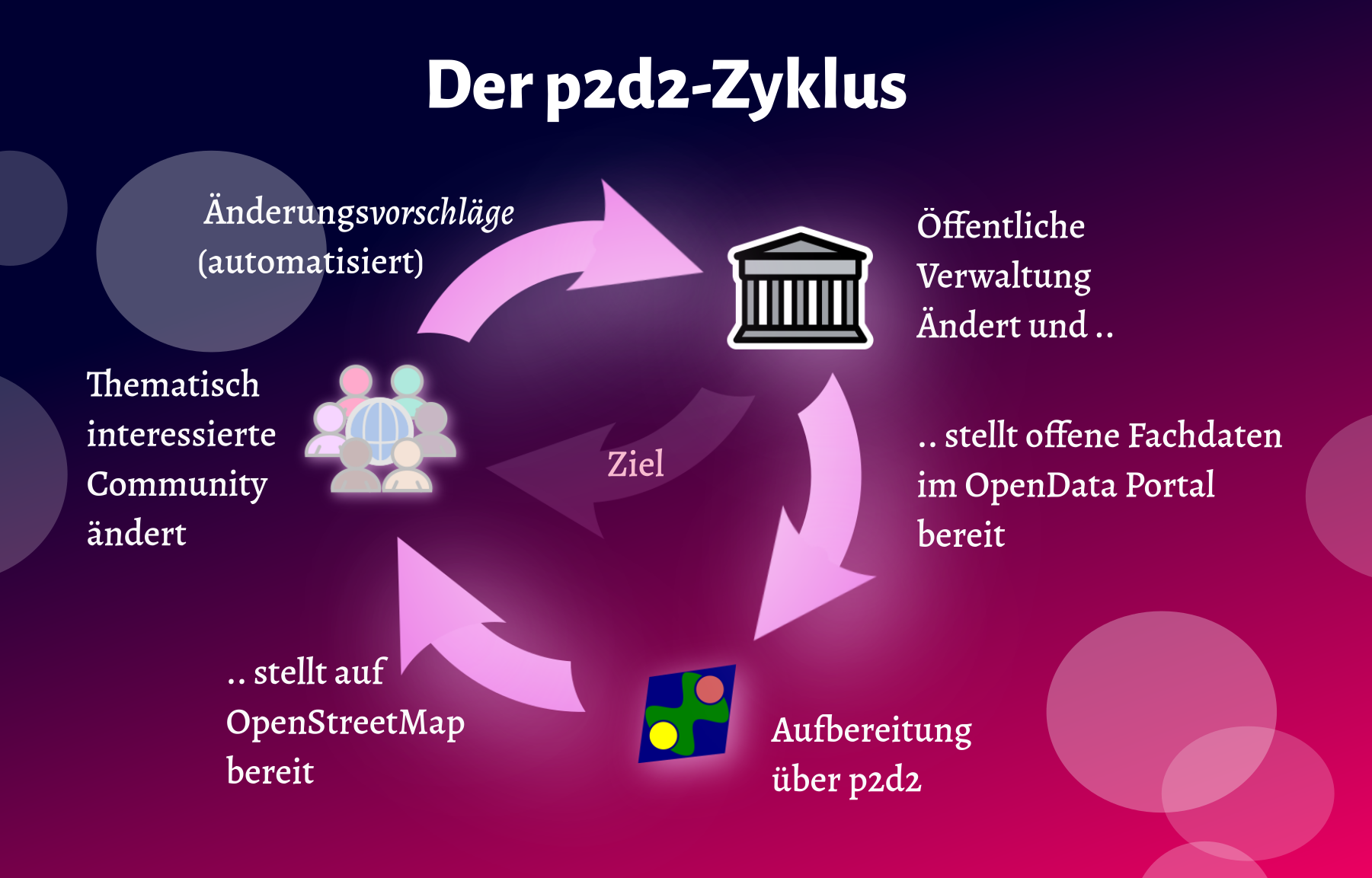 Figure: The p2d2 cycle visualizes the bidirectional data flow between administration, p2d2 community, and public platforms
Figure: The p2d2 cycle visualizes the bidirectional data flow between administration, p2d2 community, and public platforms
1. Administration Creates Data
Administrative staff collect and maintain data in specialized systems:
- Cemetery management software
- Administrative GIS systems
- Specialized databases
Example: A new cemetery is created in the municipal GIS.
2. Automated Publication
The data is automatically published in the municipality's OpenData portal:
- Export from specialized systems
- Transformation into OpenData formats (e.g., GeoJSON, CSV)
- Provision via portal API
Example: Cemetery data appears updated daily on offenedaten-koeln.de.
3. p2d2 Takes Over Data
p2d2 imports the data automatically from the OpenData portal:
- Regular synchronization (e.g., daily)
- Transformation into unified data model
- Storage in PostGIS database
Example: New cemeteries are automatically loaded into p2d2.
4. Users Edit Data
p2d2 users review and improve the data:
- Correction of geometries (boundaries, entrances)
- Addition of missing attributes
- Adding photos or descriptions
- Marking for quality assurance
Example: A user corrects the cemetery entrance and adds opening hours.
5. Community Checks Quality
The p2d2 community reviews the changes:
- Review by experienced users
- Check for completeness and consistency
- Approval for mass import to OSM/WikiData
- Or: Rejection with justification
Example: A community moderator reviews the changes and approves them.
6. Automated Transfer
After approval, the data is automatically transferred:
- OpenStreetMap: Via OSM-API or JOSM
- WikiData: Via WikiData-API
- Other platforms: Depending on configuration
Example: The corrected cemetery is imported into OSM.
7. Changes Trigger Notification
Changes to data in public platforms trigger notifications:
- OSM changesets are monitored
- WikiData edits are tracked
- Specialized department receives notification
Example: The cemetery administration is informed about the OSM change.
8. Administration Reviews Change
Administrative staff review the change:
- Verification of correctness
- Decision: Adopt or reject
- If adopted: Update in specialized system
Example: The administration adopts the corrected opening hours.
9. Full Circle: Improved Data
The improved data is now available to everyone:
- Specialized system has current data
- OpenData portal is updated
- p2d2 synchronizes the changes
- OSM/WikiData have quality-assured data
Example: The cemetery is now correctly and currently recorded in all systems.
Benefits of the Cycle
- Bidirectionality: Data flows in both directions
- Quality Assurance: Community and administration check together
- Timeliness: Changes are adopted promptly
- Transparency: All steps are traceable
- Efficiency: No more duplicate work
Technical Implementation
The cycle is enabled by various components:
- Automation: Cronjobs, webhooks, APIs
- Versioning: Git-like change history
- Notifications: Email, RSS, webhooks
- Interfaces: REST-APIs, OGC services
TIP
The p2d2 cycle is the heart of the application and distinguishes p2d2 from pure data collection tools.